Churn Meaning in Business: Calculate Customer Churn Like a Pro
Master Churn Meaning, Formulas & Reporting to Boost Retention & Revenue.
In today's hyper-competitive business landscape, understanding and managing customer churn has become the difference between sustainable growth and stagnation. For businesses across industries, churn rate calculation isn't just a metric—it's a strategic imperative that directly impacts revenue forecasting, resource allocation, and long-term viability. This comprehensive guide demystifies churn meaning in business, equipping you with precise calculation methods and actionable strategies to transform customer attrition into retention opportunities.
Key Takeaways
- Vital Metric: Churn isn't just lost customers; it's a critical health indicator. A 5% reduction in churn can increase profits by 25-95%.
- Calculation is Key: You can't manage what you don't measure. Use formulas for customer churn, revenue churn, and net churn for a complete picture.
- Actionable Insights: Use churn data to identify at-risk segments, benchmark against industry standards, and implement proactive retention strategies before it's too late.
Decoding Churn: What It Really Means for Your Business
Beyond the Buzzword: True Customer Churn Meaning
At its core, churn meaning in business refers to the rate at which customers discontinue their relationship with your company over a specific period. The customer churn meaning extends beyond simple cancellation metrics—it encompasses all forms of customer attrition, including subscription cancellations, non-renewals, reduced spending, or complete abandonment of your products or services.
The churn definition business professionals use must account for both voluntary and involuntary attrition:
- Voluntary churn: Customers actively choose to leave (e.g., canceling subscriptions)
- Involuntary churn: Customers leave due to circumstances like payment failures or account inactivity
Understanding what is churn in business requires recognizing that it's not merely a number but a reflection of customer satisfaction, product-market fit, and competitive positioning. When we define churn business leaders need, it's the percentage of customers or revenue lost during a specific timeframe.

Why Churn Rate Is Your Most Critical Health Metric
The churn rate meaning transcends basic accounting—it's a vital sign of your business's health and sustainability. What does churn rate mean in practical terms? It quantifies customer loyalty and predicts future revenue stability. Companies with high churn rates face constant pressure to acquire new customers just to maintain revenue, while those with low churn enjoy predictable growth and higher customer lifetime value.
What does churn mean in sales specifically? It represents lost opportunities for upselling, cross-selling, and referrals. A 5% reduction in churn can increase profits by 25-95% (Bain & Company), making it arguably the most leveraged metric for business improvement.
The Churn Calculation Toolkit: Formulas That Matter
Basic Churn Rate Formula: Simple Customer Churn Calculation
The fundamental churn rate formula provides a straightforward way to quantify customer attrition:
Churn Rate = (Number of Customers Lost During Period ÷ Number of Customers at Start of Period) × 100This churn formula calculates the churn percentage of customers lost. For example, if you started Q1 with 1,000 customers and lost 50, your customer churn calculation would be:
(50 ÷ 1,000) × 100 = 5% quarterly churnWhen learning how to calculate customer churn, this simple formula provides immediate insight into retention health. The customer churn formula above is the foundation for more complex calculations.
Advanced Customer Churn Rate Formula for Precision
For deeper insights, businesses often use more nuanced versions of the customer churn rate formula:
Revenue Churn Rate:
Revenue Churn = (Monthly Recurring Revenue Lost ÷ Monthly Recurring Revenue at Start of Month) × 100This customer churn rate calculation is particularly valuable for SaaS and subscription businesses where customer value varies significantly. The churn calculation formula for revenue accounts for the fact that losing high-value customers impacts revenue more than losing low-value ones.
Net Revenue Churn:
Net Revenue Churn = [(Starting MRR - Ending MRR + Expansion MRR) ÷ Starting MRR] × 100This advanced churn rate calculation formula factors in expansion revenue from existing customers, providing a more accurate picture of growth potential.

Monthly vs. Annual Churn: Timing Your Calculations
The frequency of your churn report depends on your business model and strategic needs:
Monthly Churn Calculation:
Monthly Churn Rate = (Customers Lost in Month ÷ Customers at Start of Month) × 100Monthly churn is ideal for fast-moving industries like SaaS or mobile apps where customer behavior changes rapidly. It allows for quick response to retention issues.
Annual Churn Calculation:
Annual Churn Rate = (Customers Lost in Year ÷ Customers at Start of Year) × 100Annual churn calculation provides a broader view of customer retention trends and is useful for strategic planning. The annual churn rate formula can also be calculated by compounding monthly rates:
Annual Churn = 1 - (1 - Monthly Churn Rate)^12Understanding how to calculate churn rate SaaS businesses requires recognizing that monthly and annual metrics serve different purposes—monthly for operational adjustments, annual for strategic direction.
Industry-Specific Churn Calculations
SaaS Churn: How to Calculate Churn Rate SaaS Style
Software-as-a-Service companies have unique churn characteristics that require specialized calculation approaches:
SaaS Customer Churn Rate:
SaaS Churn Rate = (Customers Canceling Subscriptions in Period ÷ Total Customers at Start of Period) × 100SaaS Revenue Churn:
SaaS Revenue Churn = (MRR Lost from Churned Customers ÷ Starting MRR) × 100When how to calculate churn rate SaaS style is discussed, it's crucial to distinguish between:
- Logo churn: Loss of customer accounts
- Revenue churn: Loss of recurring revenue
- Gross churn: Total revenue lost without considering expansion
- Net churn: Revenue lost minus expansion revenue from remaining customers
Subscriber churn rate in SaaS is particularly important because acquisition costs are high, and profitability depends on long-term customer relationships. The customer churn rate calculation for SaaS often includes cohort analysis to track how specific customer segments retain over time.
E-commerce & Subscription Models: Unique Churn Metrics
E-commerce and subscription businesses face distinct churn challenges that require tailored approaches:
E-commerce Churn Rate:
E-commerce Churn Rate = 1 - (Repeat Customers in Period ÷ Total Customers in Period)Subscription Churn Rate:
Subscription Churn Rate = (Subscriptions Canceled in Period ÷ Active Subscriptions at Start of Period) × 100For these businesses, churn percentage must be analyzed alongside:
- Purchase frequency: How often customers return
- Average order value: Revenue impact of churn
- Time between purchases: Early warning indicators
Define churn rate in e-commerce contexts must account for both complete customer loss and reduced purchase frequency. The churn calculation formula for these models often incorporates customer lifetime value projections to quantify the financial impact of attrition.
From Data to Decisions: Churn Reporting & Analysis
Building an Effective Churn Report: Key Metrics to Track
A comprehensive churn report transforms raw data into actionable insights. Essential components include:
Core Metrics:
- Customer churn rate: Percentage of customers lost
- Revenue churn rate: Percentage of revenue lost
- Net churn rate: Churn adjusted for expansion revenue
- Cohort churn rates: Retention by customer segment or signup period
- Voluntary vs. involuntary churn: Reasons for customer departure
Contextual Metrics:
- Customer lifetime value (CLV): Revenue projection per customer
- Customer acquisition cost (CAC): Investment to gain each customer
- CLV:CAC ratio: Efficiency of customer investments
- Churn by customer segment: High-risk vs. stable groups
When how to measure churn is discussed, the emphasis should be on consistency in methodology and clarity in presentation. Effective churn reporting enables quick identification of problems and opportunities.
Interpreting Churn Data: When to Act and How
Understanding what does churn rate mean in context is crucial for appropriate response:
Benchmarking Your Churn Rate:
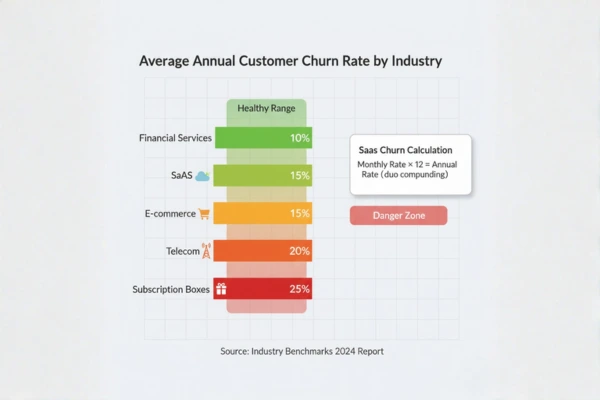
- SaaS: Acceptable annual churn ranges from 5-7% (enterprise) to 10-15% (SMB)
- E-commerce: Average monthly churn of 5-10%
- Telecom: Monthly churn of 1.5-2.5% is considered healthy
- Financial services: Annual churn of 5-10% depending on product type
Churn Rate Interpretation Guidelines:
- <5% annual: Excellent retention, focus on expansion
- 5-10% annual: Good, but monitor closely
- 10-15% annual: Concerning, requires intervention
- >15% annual: Critical, urgent action needed
Action Triggers:
- Sudden spike in churn: Investigate recent changes (product, pricing, support)
- Gradual increase: Examine customer satisfaction and competitive landscape
- Segment-specific churn: Address unique pain points for affected groups
- High-value customer churn: Immediate retention efforts
Annual churn rate formula results should be compared against industry benchmarks and historical performance to determine appropriate responses.
Reducing Churn: Strategic Actions After Calculation
Proactive Retention Tactics Based on Churn Insights
Once you've mastered churn rate calculation, the next step is implementing targeted retention strategies:
Pre-Churn Intervention:
- Predictive analytics: Identify at-risk customers using behavior patterns
- Health scoring: Quantify engagement levels to trigger interventions
- Personalized outreach: Tailored communications based on usage and value
- Proactive support: Address issues before customers consider leaving
Post-Churn Recovery:
- Exit interviews: Understand root causes of departure
- Win-back campaigns: Targeted offers for recently churned customers
- Feedback implementation: Demonstrate improvements based on former customer input
- Re-engagement sequences: Nurture churned customers for potential return
Customer Success Initiatives:
- Onboarding optimization: Ensure customers realize value quickly
- Education programs: Help customers maximize product utility
- Community building: Create networks that increase switching costs
- Regular business reviews: Demonstrate ongoing value for enterprise clients
Define churn business strategies must balance acquisition and retention efforts, with resources allocated based on churn analysis and customer lifetime value projections.
Turning Churn Rate into Growth Opportunities
Strategic businesses transform churn insights into competitive advantages:
Product Development:
- Feature prioritization: Based on requests from churned customers
- User experience improvements: Address friction points in customer journeys
- Pricing model adjustments: Align with customer value perception
- Service level enhancements: Improve support based on exit feedback
Marketing Optimization:
- Ideal customer profile refinement: Focus acquisition on stable segments
- Messaging alignment: Emphasize features that reduce churn risk
- Competitive differentiation: Highlight retention advantages
- Customer advocacy programs: Leverage satisfied customers for referrals
Operational Improvements:
- Customer journey mapping: Identify and eliminate pain points
- Cross-functional collaboration: Align product, sales, and support on retention
- Compensation structure: Reward long-term customer value over short-term gains
- Technology investments: Implement tools that enhance customer experience
Annual churn calculation should inform strategic planning, with targets set to gradually reduce attrition while increasing customer lifetime value.
Conclusion: Making Churn Calculation Your Competitive Advantage
Understanding churn meaning in business is fundamental to sustainable growth in today's customer-centric economy. By mastering churn rate calculation and implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, businesses can transform customer attrition from a challenge into an opportunity for differentiation and improvement.
Remember that effective churn management is an ongoing process—not a one-time calculation. Regular churn report analysis, combined with proactive retention initiatives, creates a virtuous cycle of customer satisfaction and business growth.
As you implement these churn formula approaches and calculation methods, focus on the insights they reveal rather than just the numbers. The true value of churn analysis lies in its ability to drive strategic decisions that enhance customer relationships and build long-term business resilience.
By making churn rate calculation a core competency, you position your business to not only retain more customers but also create experiences that turn satisfied customers into vocal advocates—fueling sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive marketplace.